Nitrous oxide, also known as laughing gas, has the chemical formula N2O and is commonly used in medical anesthesia and the food industry.
1.Chemical properties:
(1)Chemical structure: Two nitrogen atoms in a molecule are combined with one oxygen atom in a linear arrangement, and the length of the nitrogen-oxygen bond is about 1.12 Å, and the length of the nitrogen-nitrogen bond is about 1.10 Å.
(2)Physical:
Status: It is a colorless gas at room temperature with a slight sweet taste.
Boiling Point: -88.5 °C (compressible as liquid at room temperature).
Density: about 1.5 times that of air, so the specific gravity in air is lighter.
(3)Reactivity:
Decomposition reaction:
At high temperatures, nitrous oxide decomposes and reacts to produce nitrogen and oxygen
The decomposition temperature is usually above about 300 °C.
(4)Oxidation:
Nitrous oxide can act as an oxidizing agent and is able to support combustion. For example, in rocket propellant, it reacts with fuel to provide oxygen to facilitate combustion.
(5)Reactions with other substances:
Nitrous oxide can react with certain metals and non-metals to form different compounds. In catalytic reactions, N2O can react with hydrogen to produce nitrogen and water.
2.Use
(1) Anesthesia:
Nitrous oxide is often mixed with oxygen as an inhalation anesthetic and is widely used in dentistry, surgery, and emergency care. It works quickly and reduces pain and anxiety for patients.
(2) Analgesia:
In labor and emergency medical care, N2O can be used to provide rapid analgesia, especially for patients who do not wish to use general anesthesia. Its effects are short-lived and easy to control.
(3) Sedation:
N2O can be used as a mild sedative to keep the patient awake during the procedure while reducing discomfort.
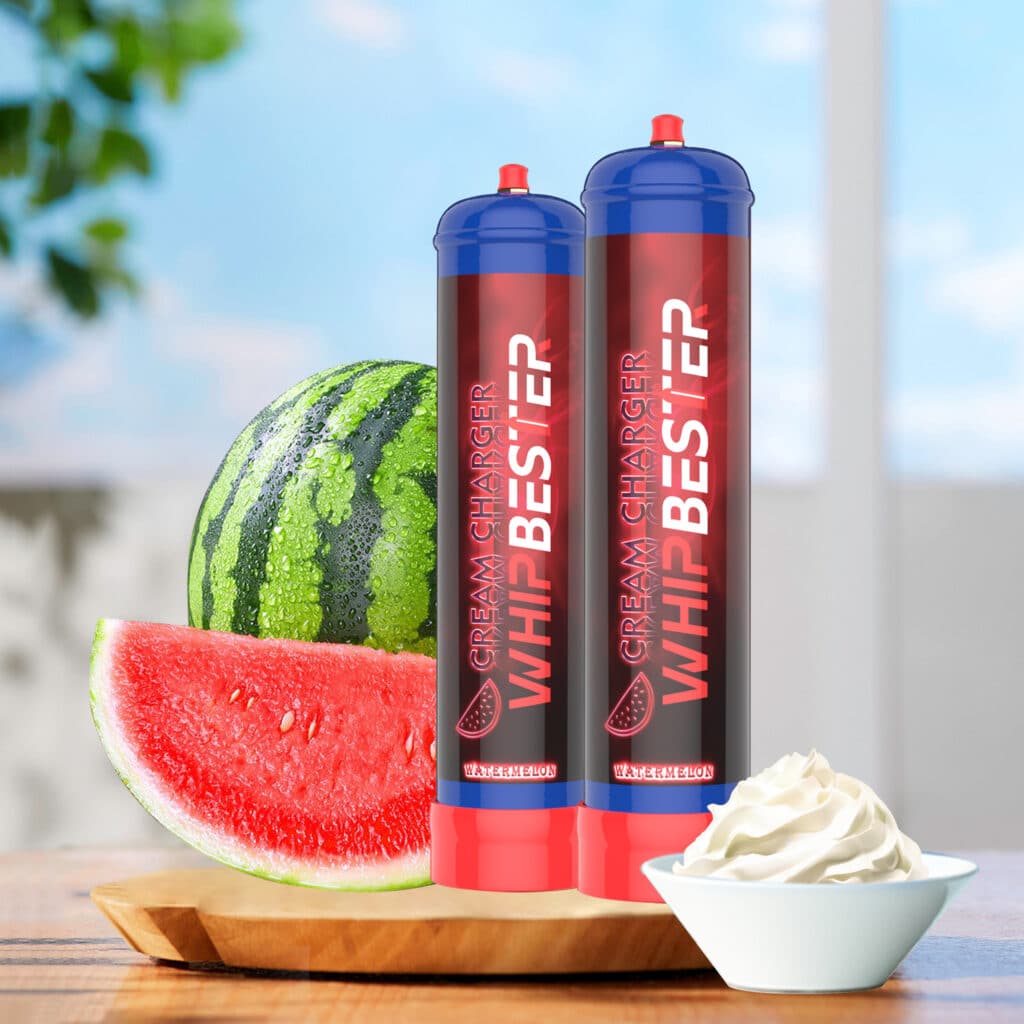
(4) Food industry
Blowing agent:
In the production of whipped cream and other food products, N2O is used as a foaming agent to form a stable foam structure and increase the taste and appearance of the food,such as whipbester N2O tank cylinders.
Thickener:
The use of N2O in some liquid foods can help improve their consistency and make the product more appealing.
Preservative:
In food packaging, N2O can replace oxygen, slow down food oxidation, and extend shelf life.

(5) Industrial use
Propellant:
In aerosol cans and other gas-driven products, N2O is used as a propellant to help release the product from the container.
Chemosynthesis:
In the chemical industry, N2O acts as an oxidizing agent and is involved in the synthesis of certain compounds, especially in catalytic reactions.
(6) Scientific research
Laboratory Uses:
In many experiments, N2O can be used to study reaction kinetics, catalytic processes, and greenhouse gas effects.